Describe How Confidence Intervals Are Used in a Statistical Study
Confidence intervals and effect sizes enhance the practical interpretation of research results. In Statistics a confidence interval is a kind of interval calculation obtained from the observed data that holds the actual value of the unknown parameter.
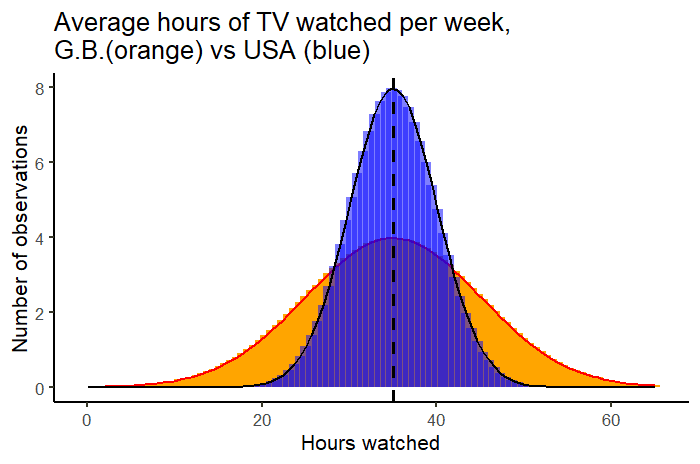
Understanding Confidence Intervals Easy Examples Formulas
-P-value summarise the strength of the evidence against null hypothesis.

. The confidence interval CI is a range of values thats likely to include a population value with a certain degree of confidence. P-value VS confidence interval. The confidence level tells you how sure you can be.
When a statistically significant difference exists between 2 means effect size is used to describe how large or small that difference actually is. The larger a 90 confidence interval for a particular estimate the more caution is required when using the estimate. Statisticians use confidence intervals to measure uncertainty in a sample variable.
It is possible to. Previous question Next question. The Form of a Confidence Interval A confidence interval consists of two parts.
For example a researcher selects different samples randomly from the same population and computes a confidence. The confidence interval is a range of values calculated by statistical methods which includes the desired true parameter for example the arithmetic mean the difference between two means the odds ratio etc with a probability defined in advance. Confidence intervals are one way to represent how good an estimate is.
A confidence interval is the mean of your estimate plus and minus the variation in that estimate. This is the range of values you expect your estimate to fall between if you redo your test within a certain level of confidence. Confidence Intervals If we want to convey the uncertainty about our point estimate we are much better served using a confidence interval CI.
It is expressed as a percentage and represents how often the true percentage of the population who would pick an answer that lies within the confidence interval. The 99 confidence level means you can be 99 certain. If n 30 use the t-table with degrees of freedom dfn-1.
Lets now apply these concepts to a specific situation. Confidence in statistics is another way to. The percentage reflects the confidence level.
The confidence interval is expressed as a percentage the most frequently quoted percentages are 90 95 and 99. In the normal course of events population standard deviations are not known and must be estimated from the data. -Confidence interval gives an idea of where the true value of what you are measuring lies.
The parameters of the population. For example if a study is 95 reliable with a confidence interval of 47-53 that means if researchers did the same study over and over and over again with samples of the whole population they would get results between 47 and 53 exactly. The interval is generally defined by its lower and upper bounds.
In a statistical study confidence intervals are used to measure the uncertainty in a sample variable. The 95 confidence level means you can be 95 certain. It is associated with the confidence level that quantifies the confidence level in which the.
Confidence interval for a proportion from one sample p with a dichotomous outcome. Clinical significance is a decision based on the practical value or relevance of a particular treatment and this may or may not involve statistical significance as an initial criterion. Identify the importance of point and interval estimates confident levels and coefficients and.
The frequency with which an observed interval eg 072288 contains the true effect is either 100 if the true effect is within the interval or 0 if not. Confidence intervals demonstrate how sure researchers are that a mean will lie between two numbers. The confidence level describes the uncertainty associated with a sampling method.
What is confidence interval - Statisticians use a confidence interval to describe the amount of uncertainty associated with a sample estimate of a population parameter. Confidence intervals are an important reminder of the limitations of the estimates. If n 30 use and use the z-table for standard normal distribution.
The 95 refers only to how often 95 confidence intervals computed from very many studies would contain the true size if all the assumptions used to compute the intervals were correct. Our point estimate lies at the center of this range. The first part is the estimate of the population parameter.
A confidence interval provides a range of values within given confidence eg 95 including the accurate value of the statistical constraint within a targeted population12 Most research uses a 95 CI but investigators can set any level eg 90 CI 99 CI13. The range of values that we use to estimate this parameter is called a confidence interval. It is often expressed in percentage.
Describe how confidence intervals are used in statistical testing. Prediction intervals apply to the situation in which a statement needs to be made about a future population that does not. Confidence intervals are most commonly used.
The concept of the confidence interval is very important in statistics hypothesis testing. Confidence intervals are one way for researchers to help decide if a particular statistical result whether significant or not may be of relevance in practice. P-values can indicate how incompatible the data are with a specified statistical model.
A confidence interval establishes an interval based on a sample that contains the true population or process parameter or metric x of the time if a random sample is drawn repeatedly from the same population. View the full answer. Confidence intervals given the same confidence level are by necessity wider if the standard deviation is estimated from limited data because of the uncertainty in this estimate.
Criticism for use of p value. A CI is a symmetrical range of values within which values of repeated similar experiments are likely to lie. One specific goal in inferential statistics involves the determination of the value of an unknown population parameter.
Confidence interval for the difference in a continuous outcome μd with two matched or paired samples. The confidence interval uses the sample to estimate the interval of probable values of the population.
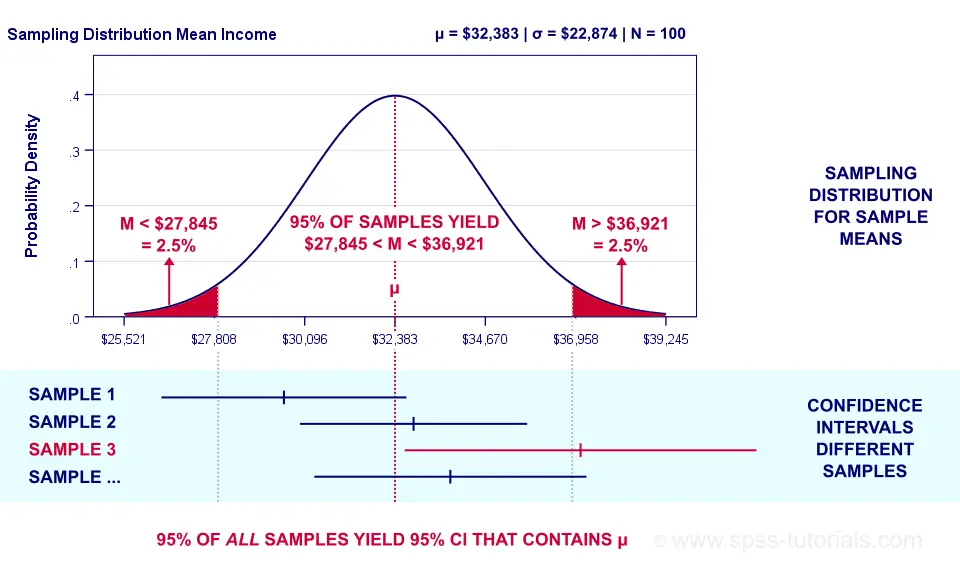
Confidence Intervals In Statistics Simple Tutorial

What Are Confidence Intervals Simply Psychology
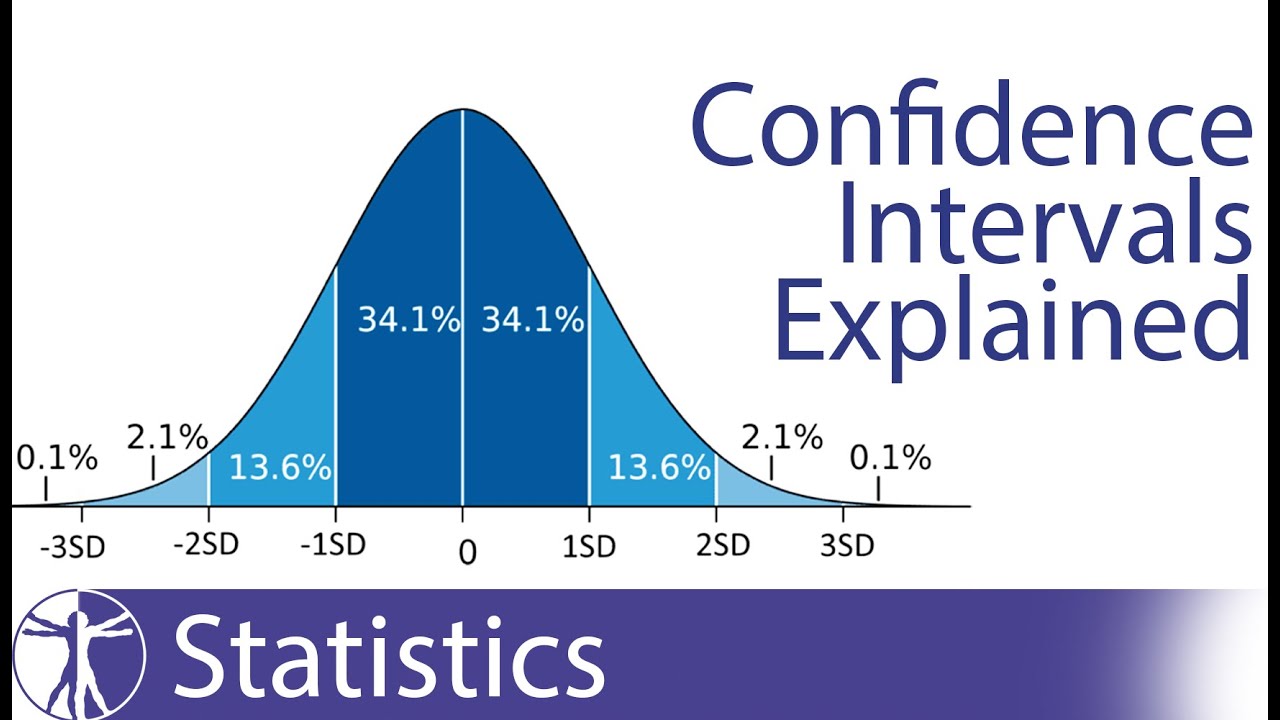
Confidence Intervals Explained Calculation Interpretation Youtube
No comments for "Describe How Confidence Intervals Are Used in a Statistical Study"
Post a Comment